Published - Wed, 20 Jul 2022
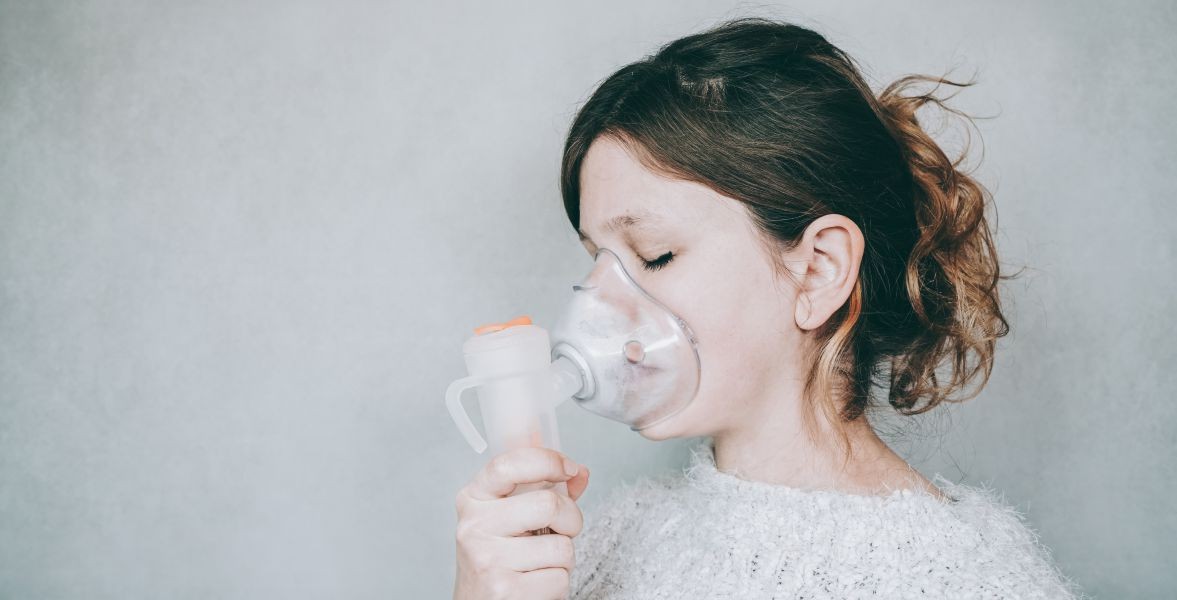

ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
Acute respiratory failure is defined as an acute impairment in oxygen or carbon dioxide exchange that results in or has the potential to result in patient morbidity or mortality. Impaired gas exchange (e.g., as a result of shunting, alveolar hypoventilation, ventilation-perfusion mismatch, or decreased pulmonary diffusion capacity) leads to hypoxemia (decreased arterial oxygen tension [PaO2]) and possibly hypoxia (i.e., insufficient delivery of oxygen to tissues). Impaired ventilation causes hypercapnia (i.e., an elevated carbon dioxide tension [PCO2]). Because the baseline respiratory status may vary greatly among patients, it is difficult to characterize acute respiratory insufficiency by purely numeric criteria.
- Generally, a patient who acutely develops a PO2 below 60 mmHg on room air or a PCO2 greater than 50 mm Hg with an arterial blood pH less than 7.35 is considered to be in respiratory failure.
- Some patients (e.g., those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD]) chronically have an elevated PCO2 but a normal arterial blood pH. In these patients, respiratory failure is defined as a PCO2 higher than baseline with a concurrent decrease in serum pH.
Causes: There are many causes of acute respiratory failure, including most pulmonary diseases as well as many cardiac diseases. Most commonly, one should consider airway obstruction, asthma, COPD, congestive heart failure (CHF), non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, pulmonary emboli, massive pleural effusion, pneumonia, hemothorax, pneumothorax, toxic inhalation, advanced lung cancer, and neurologic or muscular disorders that result in impaired respiratory abilities.
Symptoms: Dyspnea is the most common symptom of acute respiratory failure. With severe hypoxia, confusion, agitation, and disorientation might happen. Patients with significant hypercapnia frequently exhibit sluggishness or somnolence. Generalized seizures or coma may result from profound central nervous system hypoxia.
Other signs of respiratory failure include cyanosis, diaphoresis, and severely labored breathing (including the use of accessory muscles).
Children may demonstrate nasal flaring, audible grunting, or retractions (i.e., intercostal, subcostal, suprasternal).
Physical examination findings
Mild hypertension, tachypnea, and tachycardia are frequently observed.
Patients with hypercapnia may exhibit bradypnea. Wheezing, rales, or decreased breath sounds may be noted on pulmonary examination, depending on the underlying disease.
Evaluation: In a patient with suspected acute respiratory failure, patient evaluation and treatment occur simultaneously. A brief, focused clinical history and physical examination, including vital signs, will often reveal the cause of respiratory failure before obtaining any diagnostic studies.
Chest radiography helps determine the underlying cause of acute respiratory failure. At the patient's bedside, radiographs should be taken as soon as possible.
An Arterial blood gas (ABG) should be obtained in all patients with suspected acute respiratory failure. The PO2, PCO2, and pH make up the ABG's most crucial components. The patient's oxygen saturation may be measured instantly using pulse oximetry. Ancillary tests may be indicated, depending on the cause of the respiratory failure (e.g., ABG with co-oximetry for dyshemoglobinemias, an electrocardiogram [ECG] for a patient with suspected CHF, a V/Q· scan or computed tomography [CT] pulmonary angiogram for a patient with suspected pulmonary embolism, a urine toxicology screen for a patient with suspected narcotic overdose).
Therapy of Airway, breathing, circulation (ABC): Airway management, usually orotracheal intubation, is required for patients who do not have an intact airway or who are unable to protect their airway. After an airway has been established, ensuring adequate oxygenation and ventilation is the mainstay of treating respiratory failure. Patients should be administered supplemental oxygen to maintain a serum oxygen saturation of at least 90%. In addition to oxygenation, ventilation needs to be taken care of. Patients with a PCO2 greater than 50mmHg and an arterial blood pH below 7.30 require intubation and mechanical ventilation if their condition cannot be quickly improved.
Following intubation, ventilator settings for respiratory rates and tidal volumes should generally be adjusted to gradually normalize the blood pH. In general, the initial respiratory rate should be 12 to 16 breaths/min, with a tidal volume of 6 to 8 mL/kg.
Ventilation is typically less significant than oxygenation. For this reason, it is acceptable to have mild respiratory acidosis (e.g., a pH less than 7.35) if necessary to maintain adequate oxygenation or to minimize peak airway pressures.
Circulation: The placement of two peripheral intravenous lines allows the administration of fluids and medications to the patient.
Specific therapy that addresses the cause of acute respiratory failure should be undertaken after the ABCs have been addressed. In some cases, aggressive treatment of the underlying condition may reverse the respiratory failure and eliminate the need for intubation (e.g., nitroglycerin and afterload reduction for CHF, inhaled β2 agonists for asthma or COPD, chest tube placement for a large pneumothorax or hemothorax).
Disposition: All patients with acute respiratory failure should be admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU). Patients who are clinically stable but have the potential for developing respiratory failure should be admitted to an ICU or another closely monitored unit.
Created by
Rigomo Team
Rigomo is a leading online education platform that offers a wide range of courses to help individuals enhance their skills and achieve their career goals. With our user-friendly interface and expert instructors, we strive to provide high-quality education to everyone, anytime and anywhere. Join us today and take the first step towards a brighter future.
Rigomo is an e-learning platform that was founded in 2019 by a team of dedicated professionals with a passion for revolutionizing the way people learn. The platform offers a range of online courses that cover various industries, including business, technology, healthcare, and more.
Rigomo's courses are designed to be interactive and engaging, with a focus on practical skills that learners can apply in their careers. The platform uses a combination of video lectures, quizzes, and hands-on projects to help learners master the subject matter.
Rigomo is committed to providing affordable and accessible education to people around the world. The platform offers a range of pricing options, including monthly and annual subscriptions, as well as pay-as-you-go options for individual courses.
Since its launch, Rigomo has received numerous accolades for its innovative approach to e-learning. The platform has helped thousands of learners across the globe acquire new skills and advance their careers.
As Rigomo continues to grow, the team remains committed to providing high-quality education that is accessible to all. The platform is constantly updating its courses and features to ensure that learners have access to the latest tools and technologies.
Comments (0)
Search
Popular categories
Health and Wellness
231Skill Development
7Technology
5Community Impact
2Success story
2Creativity
1Latest blogs

DeepSchool: The Story of an Idea That Refused to Sit Still
Tue, 02 Dec 2025

Transforming Emergency Care: The Story Behind Rigomo's Revolutionary PPMMP Course
Sun, 12 May 2024

Empowering Rural Healthcare: How Pogiko's AI is Bridging the Gap in Medical Services
Thu, 25 Apr 2024
Write a public review